The integration of Large Language Models (LLMs) into business operations has unlocked unprecedented opportunities for innovation, from automated customer service to intelligent code generation. However, this AI revolution brings a new frontier of cybersecurity challenges that enterprises and SMEs must navigate carefully. As organizations increasingly rely on LLM APIs and Model Context Protocol (MCP) integrations, understanding and mitigating these emerging threats has become critical to maintaining secure, resilient digital infrastructures.
The New Cybersecurity Paradigm: Beyond Traditional Threats
Historically, cybersecurity efforts focused on defending against malware, network intrusions, and data breaches through established perimeter defenses and authentication protocols. The emergence of LLM APIs represents a fundamental paradigm shift, introducing threats that operate at semantic and cognitive levels rather than purely technical ones.
LLM frameworks like LangChain and LlamaIndex have revolutionized how applications collaborate and connect data. Yet these same capabilities create vulnerabilities that traditional security measures struggle to address. Unlike conventional software vulnerabilities, LLM threats exploit the probabilistic nature of AI, its limited interpretability, and its complex interaction with human language.
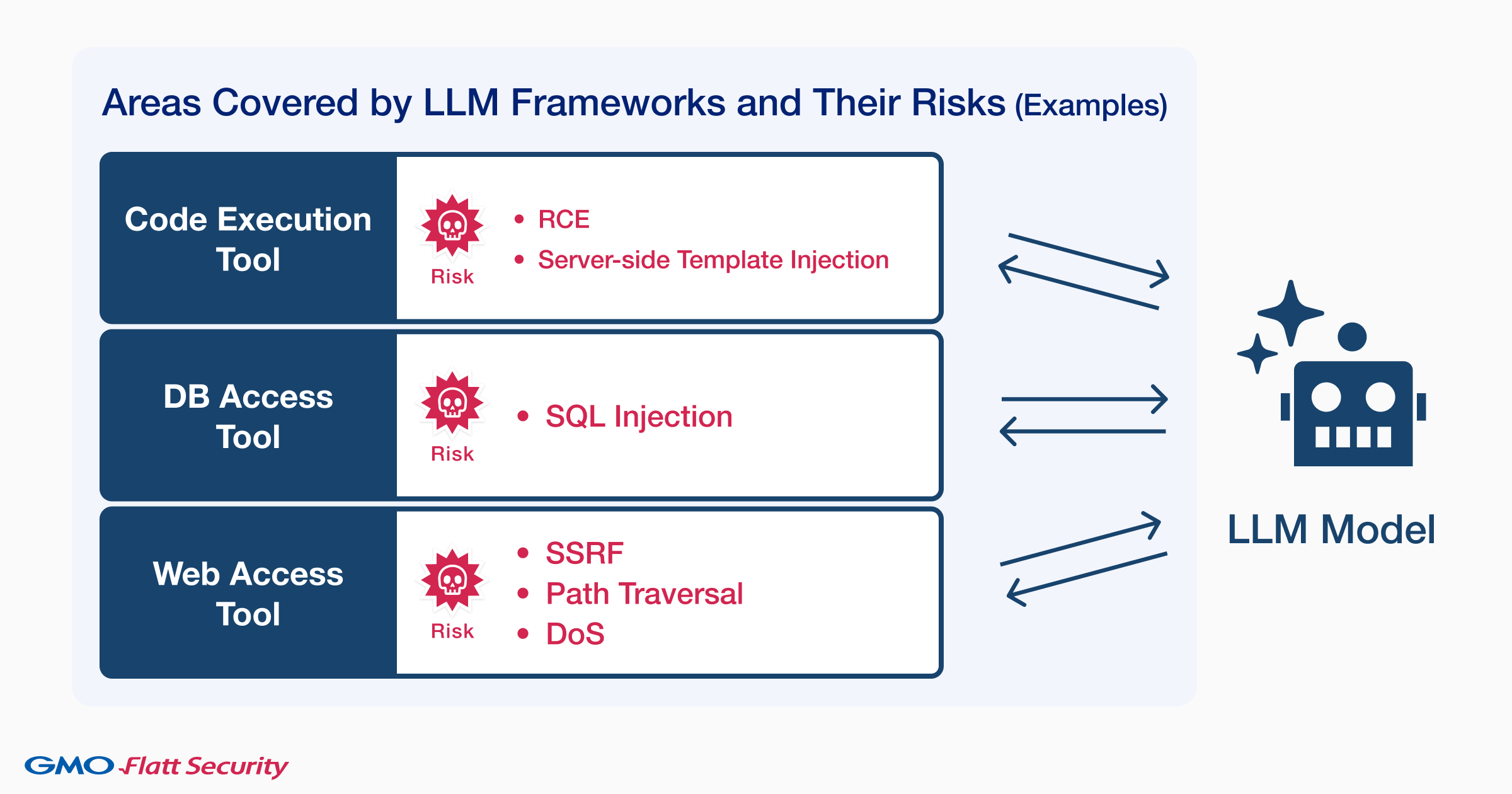
Understanding the Threat Landscape: What Makes LLM APIs Vulnerable?
The API Security Challenge
APIs serve as the critical pathways enabling LLM functionality, allowing seamless communication and data sharing between systems. However, unsecured APIs become prime targets for attackers seeking unauthorized access to sensitive information. The emergence of “shadow APIs” or “zombie APIs”, forgotten endpoints lacking current security measures, further compounds these risks.
Five Critical Threat Categories
1. Prompt Injection Attacks
Prompt injection has emerged as one of the most concerning attack vectors. Attackers craft malicious prompts that override LLM instructions or safety guidelines, forcing unintended actions, data disclosure, or harmful content generation. These attacks come in two forms:
- Direct injection: Attackers interact with the LLM to produce specific malicious responses, potentially leading to remote code execution
- Indirect injection: Exploiting model behavior without direct interaction, resulting in unauthorized data access or manipulation of AI outputs
2. Training Data Poisoning
During the development phase, malicious actors can inject biased or harmful samples into training datasets. This poisoning can occur through compromised data sources or malicious community contributions, causing models to learn dangerous behaviors that may only surface months after deployment under specific conditions.
3. API Vulnerabilities and Data Exfiltration
LLM APIs harbor latent vulnerabilities that enable sophisticated attacks including data exfiltration, API key theft, and unauthorized access. Carefully crafted prompts can extract sensitive information—proprietary code, personally identifiable information (PII), or confidential policies—that the model inadvertently exposes through its outputs.
4. Behavioral Exploitation
The stochastic behaviors of LLMs complicate traditional security monitoring methods. Integration with various systems, APIs, and plugins expands the attack surface dramatically, making detection and prevention challenging. This requires continuous behavioral monitoring and adversarial testing to identify systematic probing attempts.
5. Model Theft and Extraction
Unauthorized access or query-based extraction techniques can steal proprietary model weights, architectures, or fine-tuning data. This represents significant intellectual property loss and enables competitors or malicious actors to replicate valuable AI capabilities.

The OWASP Top 10 for LLM Applications: A Framework for Understanding Risk
The Open Web Application Security Project (OWASP) has identified ten critical risks specific to LLM applications:
- Prompt Injection – Manipulating LLM behavior to bypass safety guidelines
- Sensitive Information Disclosure – Inadvertent revelation of confidential data
- Training Data Poisoning – Compromising model integrity through malicious data
- Insecure Output Handling – Unvalidated outputs leading to downstream attacks
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities – Risks from third-party components and models
- Insecure Plugin Design – Poorly designed integrations creating attack vectors
- Excessive Agency – LLMs with autonomous capabilities being exploited
- Overreliance – Undue trust in AI outputs without sufficient oversight
- Model Theft – Attempts to steal proprietary LLM assets
- Resource Exhaustion – Malicious requests causing denial-of-service conditions
These risks represent consensus findings from major technology companies, academic institutions, and cybersecurity researchers worldwide.
Real-World Implications: Case Studies and Incidents

Enhanced Malicious Capabilities
LLMs have enabled cybercriminals to automate and scale attacks with unprecedented sophistication. Threat actors now leverage AI to generate hyper-realistic phishing emails, develop polymorphic malware, and automate vulnerability discovery—dramatically lowering the barrier to entry for sophisticated cyberattacks.
The Samsung Incident: A Wake-Up Call
A notable incident involved Samsung employees uploading confidential source code and meeting notes to public LLM services without authorization. This highlighted tangible risks of “shadow AI” usage—employees utilizing public LLM services with sensitive company data, potentially exposing proprietary information and violating compliance regulations like GDPR and CCPA.
Successful Applications in Cybersecurity
Despite these risks, LLMs show promise in enhancing cybersecurity defenses. Recent research demonstrates that properly deployed LLMs can effectively identify software vulnerabilities, automate penetration testing through chain-of-thought reasoning, and generate security patches for common weaknesses. The challenge lies in balancing these benefits against inherent security risks.
The Hidden Dangers: Shadow Systems and Overreliance
The Black Box Problem
The opacity of LLM decision-making processes presents significant challenges. This lack of interpretability hinders auditing, debugging, bias identification, and incident response. Organizations cannot fully assure the reliability of systems they cannot adequately inspect or understand.
Hallucinatory Outputs
LLMs can generate factually incorrect or fabricated information with complete confidence. Unquestioning reliance on AI outputs in critical business systems can lead to misinformed decisions, operational errors, and compromised security postures.
Building a Comprehensive Defense Strategy
Securing LLM APIs requires a holistic approach integrating technical safeguards with governance frameworks. Organizations must adopt multi-layered defense strategies:
Technical Measures
Input Validation and Sanitization
Implement rigorous filtering of malicious code, special characters, and suspicious data patterns. Employ allow-lists and integrate Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools to automatically redact sensitive information before it reaches LLM systems.
Secure API Design
Follow Secure Software Development Lifecycle (SSDLC) principles. Minimize exposed functionality by default, implement strict rate limiting and throttling, and ensure all data transmissions use TLS 1.2 or higher encryption.
Access Controls and Authentication
Deploy multi-factor authentication (MFA), OAuth 2.0 protocols, and regularly rotated API keys. Enforce least-privilege access through Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) with periodic audits to ensure appropriate permission levels.
Continuous Monitoring and Testing
Implement automated red teaming exercises, adversarial stress testing, and real-time anomaly detection. Continuous monitoring helps identify unusual patterns and potential threats before they escalate into security incidents.
Hardened Deployment Environments
Secure all components including APIs, containers, and CI/CD pipelines. Adopt effective secrets management strategies and maintain strict container image scanning protocols.
Governance and Risk Management
Comprehensive Policies
Establish clear guidelines for data handling, privacy protection, and security protocols specific to LLM usage. Define acceptable use cases and prohibited applications to prevent shadow AI proliferation.
Responsible AI Framework
Develop governance structures incorporating ethics, fairness, transparency, and accountability. Implement model risk management processes to evaluate bias, potential misuse, and alignment with organizational values.
Staff Training and Awareness
Provide ongoing education on AI-specific risks, emerging threats, and best practices. Ensure all stakeholders understand the unique security implications of LLM deployment and usage.
Human-in-the-Loop Verification
Maintain human oversight for critical applications and decisions. Integrate verification checkpoints where subject matter experts validate AI-generated outputs before implementation.
Advanced Security Techniques
AI-Powered Defenses
Deploy machine learning systems for real-time threat intelligence, predictive analytics, and automated incident response. These systems can identify subtle anomalies and deviations indicating potential attacks.
Context-Based Access Control
Implement dynamic permission systems that adjust based on real-time context including user identity, location, device posture, data sensitivity, and inferred intent.
Privacy-Enhancing Technologies
Explore federated learning, differential privacy, and data anonymization techniques to protect sensitive information while maintaining model functionality.

The Emerging Threat Horizon: What’s Next?
Research indicates a rapid evolution in LLM-related security challenges. Publications on LLM cybersecurity surged from just one in 2020 to 82 in 2023, with continued growth projected. New risk categories identified in 2025 security frameworks include “System Prompt Leakage” and “Misinformation,” reflecting increasingly sophisticated attack techniques.
Future threats will likely involve:
- Advanced multi-stage prompt injection exploiting subtle vulnerabilities in system prompts and tool integrations
- Enhanced denial-of-service attacks through computationally intensive queries
- Sophisticated inference attacks designed to reconstruct training data or reveal proprietary algorithms
- Malicious LLMs autonomously orchestrating comprehensive attack campaigns
How Origo Helps Enterprises Navigate LLM Security Challenges
At Origo, we understand that adopting AI technologies shouldn’t mean compromising security or overwhelming your existing teams. Our human-centered approach helps enterprises and SMEs integrate LLM capabilities safely and effectively.
Expertise When You Need It
Many organizations lack specialized expertise in cloud security, AI implementation, and innovation management. Origo bridges this gap by providing:
- Security assessments tailored to your specific LLM implementations and use cases
- Custom integration solutions that incorporate security best practices from inception
- Ongoing monitoring and support to adapt to evolving threat landscapes
- Training programs that empower your teams to recognize and respond to AI-specific threats
A Smooth Technology Transition
Implementing robust LLM security doesn’t require disrupting your entire infrastructure. We specialize in seamless integration that:
- Works with your existing security frameworks
- Scales appropriately for your organization size
- Balances security requirements with operational efficiency
- Provides clear visibility into AI system behaviors
Building Resilient AI Systems
Our Cloud Native, AI, and ML Development services ensure your LLM implementations are secure by design. We help you harness Machine Learning and cutting-edge generative algorithms while maintaining data-driven insights and streamlined operations protected by enterprise-grade security measures.
Taking Action: Your Path Forward
Securing LLM APIs is not a one-time project but an ongoing commitment requiring vigilance, adaptation, and expertise. As the threat landscape evolves, organizations must:
- Assess current LLM usage across your organization, including shadow AI implementations
- Implement comprehensive security frameworks combining technical and governance measures
- Establish continuous monitoring with AI-specific threat detection capabilities
- Maintain human oversight for critical applications and decisions
- Stay informed about emerging threats and mitigation strategies
The integration of LLMs into business operations offers tremendous potential for innovation and efficiency. However, realizing these benefits requires a proactive, comprehensive approach to security that addresses the unique challenges these technologies present.

Ready to secure your AI initiatives? Contact Origo today to discover how our human-centered approach can help your organization harness LLM capabilities safely and responsibly. We provide the expertise, tools, and support needed to navigate the complex landscape of AI security—so you can innovate with confidence.

For more information, contact us at info@origo.ec